How to Choose Between Traditional, Converged, and Hyper Converged Infrastructure
Hyper-converged infrastructures (HCI) are becoming a buzz phrase within technical circles. It has already become very popular and adopted by numerous companies because of the wide range of business needs it satisfies.
The HCI market is expected to reach $13,211 million in 2023 with a CAGR growth of 48.4% starting from 2015. The technology enables enterprises a more centralized way to manage their IT infrastructure at reduced expenses.
HCI is still a developing technology and it is still going through many transformations. Every business has different needs and it may be debatable if everyone will benefit from a HCI solution. It is not a fit for all solutions, and may need customizations.
The kind of infrastructure your business needs will depend on a lot of factors. There are major differences between the converged, hyper-converged, and the traditional infrastructure. You should know the advantages and nuances of all of them so that you can pick the best infrastructure for your business.
How to choose the Right Infrastructure for your Business?
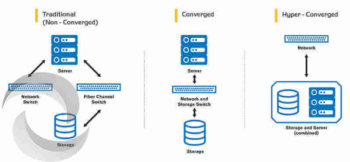
Traditional Infrastructures
Traditional infrastructures consist of separate units like the storage servers, networking, and backup appliances, application servers, and so on. They can be bought from a single vendor or come from different ones.
All the components in a traditional infrastructure are interlinked but need to be configured individually. Each separate component has to be managed separately and usually requires IT experts specializing in different fields.
Traditional infrastructures are still good for enterprises that have a stable environment and deal with huge deployments. Such companies may run multiple applications that run into thousands and tens of petabytes of data. Traditional infrastructures also easily accommodate a large number of users.
Such infrastructures are useful for multinational companies having very large operations or big data centers with unlimited processes.
Converged Infrastructure
The traditional infrastructures generally come with a controller and a rack of shelves which house the HDD or SSD arrays. In converged infrastructure all of those are consolidated into one storage platform based on nodes which delivers unmatched redundancy. This reduces the cost of maintenance and support and saves much of IT expenses.
Though all of them are consolidated in a box, you have to manage each component separately. It is composed of standalone components which can be separated from the infrastructure making it a plug and play option.
The storage server, application server, and networking appliances are included in a single box and provided by a single vendor generally as a turnkey solution. The optimized system with centralized management and consolidation into one unit delivers increased agility and efficiency.
The infrastructure can be scaled by adding more nodes when need arises. If the components are from different providers, then they have to be separately contacted in case of hardware failures.
The entire infrastructure is preconfigured to run a specific kind of workload and is less flexible when it comes to adapting to other types of workloads. The converged infrastructure can be bought in a wide range of sizes.
You can find hybrid arrays or all flash version of the storage component on converged systems. Organizations who already have a computing and network platform will find it beneficial, as deployment of varying types of storage for virtual machines will be possible. The organization can offload the workload over to a converged infrastructure eliminating the need of adding another shelf.
Converged infrastructure is suitable for enterprises that require complete control over each component of the IT system. They can adjust or customize them to serve specific needs when required.
Converged infrastructure is also suitable for complete IT overhaul as all components can be bought together. There is no need to search around for each element separately in the market.
Hyper Converged Infrastructure
HCI is now being touted as the future of data centers. HCI brings computing, storage, and networking capabilities in a single unit which are all connected with a common fabric. All the resources of the system are controlled by software and you cannot manage each component separately.
The HCI is available from a single vendor, like Greentec Systems, who is responsible for providing support both for hardware and software issues. The platform comes pre-configured and it takes less time to deploy the solution as all technologies are integrated into one. As a result operational costs are reduced along with complexities and interoperability.
The system runs on a hypervisor which is the foundation for all virtualization the system carries out. HCI platforms are also loaded with advanced data services and can be connected with third party applications easily. It delivers streamlined acquisition, support, deployment and management, bringing down expenses and improving productivity and profitability.
HCI offers cost effectiveness and increased efficiency with faster response times and greater accuracy. It is suitable for industries which need less time to market and depend on advanced computation of data.
Another plus point of HCI is its ease of scaling. It can easily be scaled by connecting additional units, eliminating over or under-purchasing. HCI platforms even bring down the TCO up to 50% and create an environment that keeps costs low. Contact Greentec Systems for further help.
As the platform is composed of a single stack of combined technologies, there are less moving parts. This translates into fewer chances of complications or hardware issues.
Difference between Traditional, Converged and Hyper Converged Infrastructure
To make you understand better, we are going to highlight the key differences between the three technologies.
In the case of traditional infrastructures, the physical servers are responsible for operating a virtualization hypervisor that controls the virtual machines built on the server. Three options are available when it comes to data– network-attached storage, or NAS, direct-attached storage, or DAS and storage-area network, or SAN.
With converged infrastructures, the physical server is responsible for storage which is generally flash storage.
HCI has a software-defined storage concept as each node in the cluster runs storage controller function as a service. Data that are accessed frequently are generally stored locally while the actual servers store important data.
Now you know the differences and nuances of the three technologies and can confidently decide on the type of infrastructure that you will need for your enterprise.